Credit Card Issuers: Drive Down Costs Before Loan Losses Rise
- Date:July 08, 2022
- Author(s):
- Brian Riley
- Research Topic(s):
- Credit
- PAID CONTENT
Overview
Recent challenges create operational risk for credit card issuers.
Credit card issuers have been resilient since the onset of COVID-19 in early 2020. Credit card loan loss reserves, which conformed to more conservative requirements after Dodd-Frank, helped cushion interest revenue shortfalls caused by shifts in consumer purchasing. Government programs such as the CARES Act shielded consumers with payment deferrals and boosted savings accounts with stimulus funds to ensure household stability. But, two years after the onset of COVID-19, global economies face surging inflation, rising interest rates, and geopolitical disruption.
In this report, we review the current condition of U.S. credit cards, identify income and expense categories, and suggest where issuers may find opportunities by tuning revenue lines or decreasing expense lines.
"Credit card revenue rebounded after COVID-19, but now net income faces another hurdle. Across the globe, economies are contending with record-high inflation, rising interest rates, and geopolitical instability. As households juggle budgets and credit card issuers build revolving debt balances, the latter must focus on fundamental revenue components and servicing costs as they contend with higher risks and the potential for more considerable credit losses," comments Brian Riley, Director of the Credit practice at Mercator Advisory Group, and the author of the research report.
This document contains 26 pages and 10 exhibits.
Companies mentioned in this research note include: American Express, Bank of America, Barclaycard, Barclays US, Bureau of Labor Statistics, Capital One, Chase, Citigroup, Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB), Discover Financial Services, FDIC, Federal Reserve Bank, Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland, Federal Reserve Bank of New York, Fifth Third Bank Corp, FIS, Fiserv, Goldman Sachs Group, JP Morgan Chase & Co., KeyBank, Mastercard, Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC), PSCU, Synchrony, TransUnion, TSYS, U.S. Bank, University of Michigan, Visa, Wells Fargo
One of the exhibits included in this report:
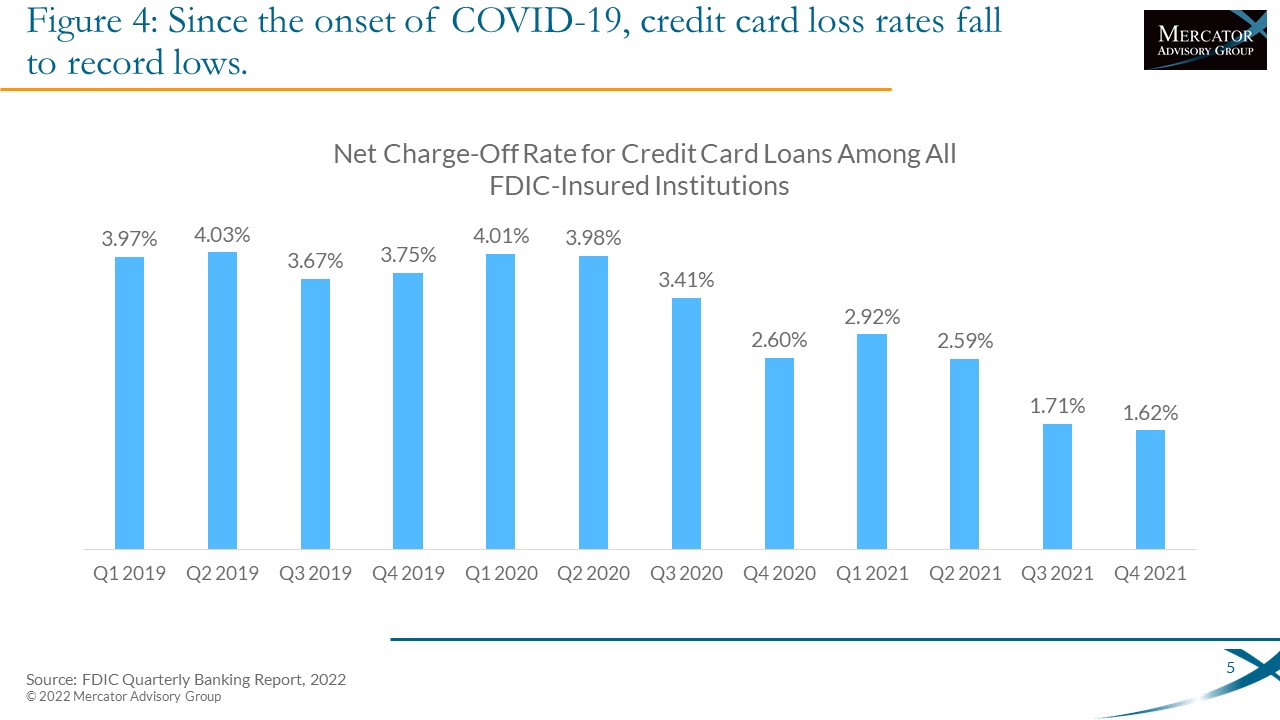
Highlights of this document include:
- Background for the Credit Card Industry
- The Good News
- Current Risks
- Strategies to Combat Rising Costs
- Recommendations
Book a Meeting with the Author
Related content
2026 Credit Card Risk: Happy Days are Here Again (For Top Issuers)
The year bodes well as 2026 approaches the end of the first quarter. Economic indicators are strong, the credit card market is growing at a healthy rate, and credit cards rem...
Credit Card Databook 2026
The credit card market, which appeared to be a candidate for saturation in recent years, continues to grow amid a resilient economy. Purchase volume reached $1.28 trillion in 2025,...
Chase Bites on Apple: Big Gets Bigger (and Probably Better)
JPMorgan Chase’s deal with Goldman Sachs to take over stewardship of the Apple Card sends both banks in the direction of their greatest strengths. JPMorgan Chase knows how to run a...
Make informed decisions in a digital financial world